 |
 |
In contrast, P2Cast clients not only receive the requested stream, but also
contribute to the overall VoD service by forwarding the stream to other
clients and caching and serving the initial part of the stream.
Associated with P2Cast is a
threshold, ![]() .
The clients that arrive within the threshold constitute a
session. Together with the server, clients belonging to the same
session form an application-level multicast tree, denoted as
the base tree. The server streams the entire video over the base
tree.
We denote this complete video stream as
the base stream. When a
new client joins the session, it joins the base tree and retrieves the base
stream from it. Meanwhile, the new client must obtain a ``patch'' - the
initial part of the video from the start of the session to the time
it joined the base tree. As we will see, it
obtains the patch from the server or another client.
P2Cast clients behave like peers in a P2P network,
and provide the following two functions:
.
The clients that arrive within the threshold constitute a
session. Together with the server, clients belonging to the same
session form an application-level multicast tree, denoted as
the base tree. The server streams the entire video over the base
tree.
We denote this complete video stream as
the base stream. When a
new client joins the session, it joins the base tree and retrieves the base
stream from it. Meanwhile, the new client must obtain a ``patch'' - the
initial part of the video from the start of the session to the time
it joined the base tree. As we will see, it
obtains the patch from the server or another client.
P2Cast clients behave like peers in a P2P network,
and provide the following two functions:
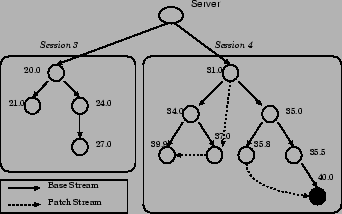
We use an example to illustrate P2Cast. Fig. 1 illustrates a snapshot of P2Cast at time 40. It shows two sessions, session 3 and session 4, starting at time 20.0 and 31.0, respectively, with the threshold equal to 10. We use circles to represent clients with the client's arrival time marked beside the circle. A solid line with an arrow is used to represent the parent-child relationship in the base tree; and a dashed line with an arrow is used to represent the patch server-client relationship. The server and the clients in a session form an application-level multicast tree to deliver the base stream. At time 40, all clients in session 3 have finished the patch retrieval; while three clients in session 4 are still in the process of receiving the patch stream. Note that clients belonging to different sessions are independent of each other. In Section 5 we will use this observation to improve the clients' robustness against the disruptions caused by the clients' early departure.
We describe below a new client admission process, the base tree construction/joining process, the patch server selection process, and the failure recovery process, respectively.