


Next: Notations and performance metrics
Up: Performance Evaluation
Previous: Performance Evaluation
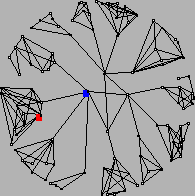
We use a 3-level network topology in our simulation
experiment. Fig. 3 illustrates the top two levels
generated by GT-ITM [12] with 100 nodes. We assume that
each node is an abstraction of a local
network that can host an unlimited number of clients, and there is sufficient bandwidth
within a local network to support media streaming. The network
consists of one transit network (consisting of 4 nodes) and 12 stub
domains. The shortest path
algorithm is used to determine the routing.
We assume that the video playback rate is constant bit rate (CBR).
We assign a bandwidth to each link in terms of the
number of playback rate a link can support.
The capacities of links between
transit nodes and between transit nodes
and stub domain nodes are chosen to be larger than those between
stub domain nodes, since links in
the core network are typically better provisioned and have more bandwidth than
the edge links.
Using advanced coding techniques, videos with the playback rate from
300bps to 500bps offer
reasonably good viewing quality. A link with the capacity of 100Mbps
can support 200 to 333 such streams. Since we simulate
P2Cast providing service for
one video, we choose the capacity of each core link to be
20, i.e., core links can support up to 20 streams simultaneously; and that
of each edge link to be 5 for the simulation results reported in this
paper.
Furthermore, we change the location of server from the transit network to
the stub domain to study the sensitivity of the performance to the server
bandwidth change. We also vary the link capacity, and
similar results are observed in [11].
We simulate the on-demand service of one video to clients whose arrival process
is Poisson. Each client is equally likely to be placed at any node.
It is possible for
more than one client to reside at the same node.
Figure 3:
Top 2-level network topology used in simulation.
 |



Next: Notations and performance metrics
Up: Performance Evaluation
Previous: Performance Evaluation
Yang Guo
2003-03-27
