
Figure 1: The Epidaurus Theatre
An open, application for enabling prototyping and delivery of virtual learning experiences through the Internet is presented. VRML and Java are the key technologies.
Application Enigma has been developed and tested based on 3D content developed by the Foundation of the Hellenic World (FHW). This content represents the ancient theatre of Epidaurus (Figure 1), as well as a part of the ancient city of Priene.

Figure 1: The Epidaurus Theatre
Small-scale partitioning techniques have been applied, especially in the case of Priene, where the VRML files are huge. The streams produced by the guide and transmitted to the users are:
Enigma enables groups of users to monitor multimedia-rich virtual guided tour sessions inside 3D representations of archaeological sites. A live guide controls these sessions so that all users have the same view of the content, as shown in figure 2, while also explaining to them through live voice. An object inside the VRML scene can be used as a pointer indicating the objects of interest that the guide presents while speaking.
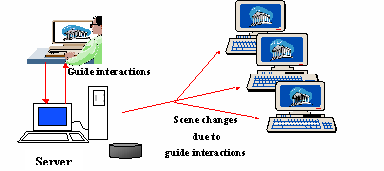
Figure 2: Enigma interactivity
Java based extensions, such as the External Authoring Interface (EAI) [1], and the Java Media Framework (JMF) [2] are exploited to integrate all the different media streams. The JMF API implements streaming media over the RTP/RTCP protocols. EAI enables to control the position and orientation of the camera or certain objects in the 3D scene.
Virtual representations of monuments can be huge in terms of size and rendering requirements and thus unsuitable for the network, as VRML format is uncompressed, downloading times can be big and/or rendering and navigation can be hard.
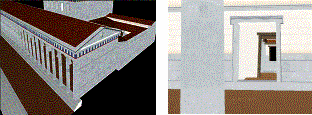
Figure 3: Small scale scene partitioning
.JMF handles intra-stream and inter-stream synchronization of continuous flows (audio, video) based on the RTP protocol (through timestamps) and by implementing buffering schemes at the receiver. Therefore, inter-stream synchronization between continuous and discrete media flows, as well as inter-user synchronization must be achieved through application specific implementations.
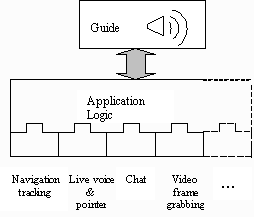
Figure 4: Extensible Architecture
Educative, networked virtual reality applications based on cultural heritage or other content have appeared so far, such as the one described in [3]. However, these are customized for certain virtual reality display systems, such as CAVE and ImmersaDesk, which are too expensive to be widely applied.
This work is partly funded by the IST ADAMANT European Research Project.