Kokono Search: A Location Based Search Engine
Seiji YOKOJI
NTT
3-9-11, Midori-cho, Musashino-shi, 180-8585, Tokyo, Japan
+81-422-59-2983
yokoji.seiji@lab.ntt.co.jp
|
Katsumi TAKAHASHI
NTT
3-9-11, Midori-cho, Musashino-shi, 180-8585, Tokyo, Japan
+81-422-59-2863
takahashi.katsumi@lab.ntt.co.jp
|
Nobuyuki MIURA
NTT DoCoMo
3-5, Hikarino-oka, Yokosuka-shi,239-8536, Kanagawa, Japan
+81-468-40-3809
miura@mml.yrp.nttdocomo.co.jp
|
ABSTRACT
We have developed a location-based search system for web documents on
the Internet.
This system can find web documents based on the distance between
locations that are described in web documents and a location specified
by a user.
It consists of three modules.
(1) A robot that gathers documents from the Internet,
(2) a parser that extracts address strings from web documents and
associates latitude-longitude information to the original document and
(3) a retrieval module.
This system can retrieve location-related web documents overlooked by
conventional keyword-based search engines.
Keyword-based search engine overlooked more than 25% of location-related
web documents compared with our search engine.
We have served this location-based search as an experimental
service named kokono search that is one of Mobile Info. Search
[1],[2]
services on the Internet.
Keywords
Location-based search, Information extraction, Search engine,
Selective gathering, Information integration, Information retrieval,
Web robot
1. INTRODUCTION
Recently, it has become possible to browse real world information, such
as telephone directories, maps, town-guides, tourist-guides and
shop-guides through an open-network like the Internet.
Each of these sources is related to geographical locations and can be
classified by using user location data such as the current location,
user's destination and the user's residential address.
There are already many search engines [3] on the Internet, and most of them are
keyword-based.
Basically, when we attempt to search real world information about
a specific geographical location, information about nearer
locations from the specified location is more important.
Unfortunately ,there are many cases that neighboring geographical
regions have different addresses (i.e. keyword).
Therefore, keyword-based search may overlook useful information about
locations that are adjacent to the specified location.
To solve these problems, we developed location-based search
engine.
We define the location-based search as a search method based on
the distance between a user-specified location and locations that are
described in web documents. Locations are represented as address
strings, telephone numbers, rail station name etc. in web documents.
Our system converts them to latitude-longitude pairs or polygons consist
of latitude-longitude pairs.
Also a user-specified location is represented as a latitude-longitude pair.
By using these latitude-longitude pairs to retrieve documents, our
system finds documents about nearer locations from a specified location.
2. LOCATION-BASED SEARCH ENGINE
This system consists of following three components.
- The robot gathers web documents from the Internet.
After a document was gathered, the robot prioritizes URLs that were
included in it.
For example, the priority is high when a link label contains location
information (ex. Address etc.) Then the robot gathers web documents that
have high priority.
- A parser extracts location information from web documents and
converts them into latitude-longitude pairs or polygons.
- The retrieval module converts location information specified by user
to a latitude-longitude pair and it creates a search circle whose center
is this pair.
By judging overlaps of this circle and the latitude-longitude pairs or
polygons, it picks up documents that are written about locations within
this circle.
The engine returns URLs of the documents as results of the search. The
module calculates the radius of the circle automatically that the
overlaps contain appropriate number of results.
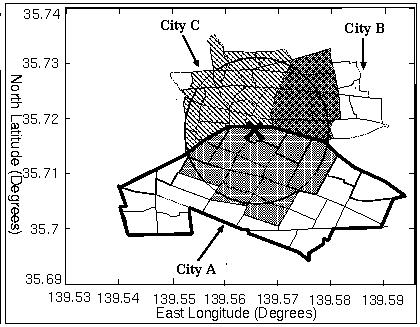
Fig 1 An example of geographical regions searched
by "location-based search" and "keyword-based search"
Figure 1 shows an example of geographical region searched by both search
methods.
The cross sign is the user-specified location. Keyword-based search
engine retrieves documents about region enclosed by thick line.
Although there are latitude-longitude pairs and polygons that are close
to the cross sign and belong city 'B' or 'C', the documents about these
locations cannot be found by the keyword-based search.
On the contrary, location-based searchretrieves the documents
about the region represented as meshed polygons.
This region contains all latitude-longitude pairs and polygons that are
close enough to the cross sign.
As the result, we can also find location-related web documents
overlooked by keyword-based search engine, when we use our
location-based search engine.
3. REFERENCES
-
Katsumi Takahashi.
A Mobile Portal Service to Provide Location Dependent Information.
In Proc. from the Joint W3C-WAP Forum workshop on "Position dependent
information services"
(Feb, 2000)
-
Mobile Info. Search.
http://www.kokono.net/english/
-
Google , http://www.google.com/

